
- #Elasticsearch filebeat docker how to#
- #Elasticsearch filebeat docker install#
- #Elasticsearch filebeat docker password#
- #Elasticsearch filebeat docker plus#
#Elasticsearch filebeat docker install#
RUN curl -o /tmp/filebeat_1.0.1_b & \ĭpkg -i /tmp/filebeat_1.0.1_b & apt-get installĬOPY filebeat.yml /etc/filebeat/filebeat.ymlĪs you see, we download and install the package first, then copy the config to image.
To do so let’s add these lines to Dockerfile:
#Elasticsearch filebeat docker password#
Then make sure no other services are running with same name by shutting them down with docker-compose down command, as if we had it from previous part of this tutorial, docker-compose would fails during creation of services.Then we set up password for artifactory, I could have committed it, but I am a bit paranoiac about committing passwords to repo.
#Elasticsearch filebeat docker plus#
We firstly download all images needed to prepare our environment, plus make maven available for Jenkins container. #update older jenkins image, make sure it doesnt use cache #clean anything with same name to get rid of clashesĮcho "password" >. Git checkout dockerizing_jenkins_part_3_docker_compose_docker_secret_credentials_plugin & \

First thing first, let’s checkout the project: In this example we will use Jenkins image we created earlier in the part 3 of these series.
Prepare our dockerized dev environment with Jenkins, Sonarqube and JFrog artifactory running the declarative pipeline
#Elasticsearch filebeat docker how to#
Configure Filebeat so it knows how and where collect the Jenkins logs and how to send them further to logstash.Download and install Filebeat on our Jenkins image.Prepare our dockerized dev environment with Jenkins, Sonarqube and JFrog artifactory running the declarative pipeline.So the summary of what we are going to look at today is: I also wanted to demonstrate how we can install anything on our Jenkins image, so it is more interesting. In our example we will try to use all of them, plus, we won’t be running Filebeat in a separate container, but instead, will install it right inside of our Jenkins image, because Filebeat is small enough.

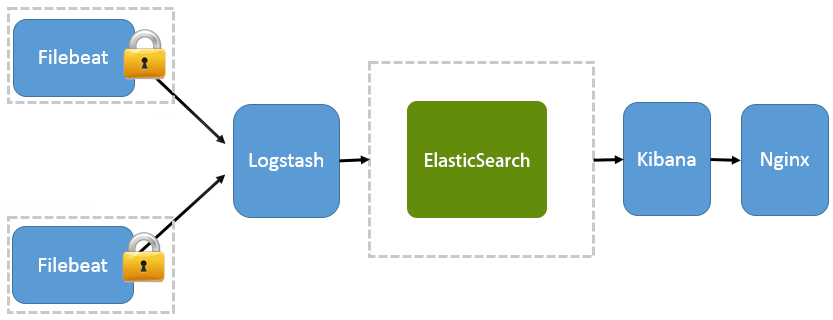
In fact, if you don’t have any filtering and parsing requirements you can skip the logstash at all and use Filebeat’s elastic output for sending the logs directly to elasticsearch. On top of that, because logstash is heavyweight jruby app on JVM, you either skip it at all or use a way smaller application called Filebeat, which is a logstash log forwarder, all it does, collects the logs and sends to longstash for further processing. The Idea with ELK stack is you collect logs with Filebeat(or any other *beat), parse, filter logs with longstash and then send them to elasticsearch for persistence, and then view them in kibana. We also will be running Jenkins in Docker, meaning if container is dropped and no other means are in place, like mounting the volume for logs from a host and taking the backup the logs will be lost.Īs you may have already heard, one of the best solutions when it comes to logging is called ELK stack. Our aim in this article will be persisting the logs in a centralised fashion, just like any other application logs, so it could be searched, viewed and monitored from single location. Depending on a log rotation configuration, the logs could be saved for N number of builds, days, etc, meaning the old jobs logs will be lost. Normally, in order to view the build logs in Jenkins, all you have to do is to go to particular job and check the logs. Today we are going to look at managing the Jenkins build logs in a dockerized environment. This is 4th part of Dockerizing Jenkins series, you can find more about previous parts here:ĭockerizing Jenkins, Part 1: Declarative Build Pipeline With SonarQube Analysisĭockerizing Jenkins, part 2: Deployment with maven and JFrog Artifactoryĭockerizing Jenkins, part 3: Securing password with docker-compose, docker-secret and jenkins credentials plugin


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
